Summary
In today`s interconnected world, the security of IoT devices has become crucial as cyber threats continue to evolve. This article delves into essential strategies for protecting these devices, offering valuable insights that can resonate with anyone concerned about cybersecurity. Key Points:
- Embrace Zero Trust Architecture to ensure every IoT device is continuously authenticated and authorized, moving away from traditional perimeter security.
- Leverage AI-driven threat detection to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities by utilizing advanced analytics for real-time monitoring and response.
- Adopt quantum-resistant cryptography to safeguard your devices against future threats posed by advancements in quantum computing.
What is IoT Security and Why It Matters
To effectively protect these interconnected devices, organizations must implement specific technologies such as end-to-end encryption and robust device authentication protocols. Secure firmware updates are also critical in defending against potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Furthermore, physical security measures should not be overlooked; protecting devices from tampering is just as vital as digital safeguards. Real-world examples of cyber threats targeting IoT devices highlight the importance of these strategies in preserving personal data and maintaining overall system reliability. In summary, enhancing IoT security is a necessity for organizations navigating this rapidly evolving landscape.
The Growth of IoT Devices and Associated Risks
To mitigate the risks associated with these vulnerabilities, employing robust encryption protocols like AES and TLS is crucial for securing data transmission between devices. Additionally, integrating hardware security measures such as Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) can help ensure the integrity of these devices. Regularly updating firmware is another essential practice that helps patch potential security holes.
Moreover, as the technology behind these devices evolves, emerging materials—such as advanced polymers or antimicrobial coatings—are being explored to enhance both functionality and security. By addressing both software and hardware aspects of device safety, we can better protect our increasingly connected world from cyber threats.
| IoT Security Challenges | Key Strategies | Emerging Trends | Real-World Examples | Career Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vulnerabilities due to inadequate encryption and authentication methods | Implement end-to-end encryption and robust device authentication protocols | Adoption of Zero Trust Architecture for enhanced security verification | Notable incidents involving compromised IoT devices like security cameras leading to network breaches | Growing demand for cybersecurity professionals specializing in IoT security |
| Physical tampering risks and lack of regular firmware updates | Regularly update firmware and conduct vulnerability assessments to patch weaknesses | Exploration of advanced materials (e.g., antimicrobial coatings) to improve device safety | Case studies showing how poor configurations led to severe vulnerabilities across multiple sectors | Certification paths like CISSP or CCGP™ for aspiring cybersecurity experts |
| Remote exposure increasing attack surfaces for hackers | Utilize defense-in-depth strategies involving layered security measures | Integration of AI-driven analytics for real-time threat detection | Examples where organizations faced data breaches due to lax IoT device configurations | Importance of continuous learning in emerging technologies related to IoT security |
| Interconnectedness creating single points of failure within networks | Employ strong encryption protocols during data transmission and storage | Focus on edge computing trends that influence the future of IoT security roles | Highlighted instances where attackers exploited unsecured APIs in popular consumer products | Opportunities for skill development in machine learning algorithms designed for threat detection |
Understanding the Importance of IoT Security in 2025
## The Importance of IoT Security in 2025
The scope of IoT encompasses an extensive range of devices, from smartwatches and thermostats to video game consoles and beyond. To effectively safeguard these devices, adopting frameworks like Zero Trust Architecture is essential; it requires that every device and user be verified before access is granted. Furthermore, implementing advanced encryption techniques such as AES-256 can help maintain data integrity during transmission.
Continuous monitoring through AI-driven analytics plays a pivotal role in enabling real-time threat detection, which is crucial as the landscape evolves. Additionally, regular firmware updates and diligent patch management are vital practices to address vulnerabilities promptly and efficiently. Taking these proactive measures will significantly enhance IoT security in the coming years.
Identifying Vulnerable IoT Devices in 2024
To effectively tackle these challenges, it’s crucial to assess specific parameters that can reveal device vulnerabilities. Evaluating firmware versions, encryption standards, and authentication methods will enhance understanding of potential weaknesses. Additionally, considering the materials used in device construction may provide insight into their susceptibility to physical tampering or environmental conditions. Regular vulnerability assessments and timely updates should also be part of a proactive security strategy aimed at identifying and mitigating risks associated with IoT devices.
 Free Images
Free ImagesKey Challenges Facing IoT Security Today
## Which IoT Devices Are Most Vulnerable?
As highlighted in the "Riskiest Connected Devices in 2024" report by Forescout Research, certain categories of devices are particularly susceptible to cyberattacks.
## Challenges in IoT Security
The multitude of connection methods available for IoT devices increases the likelihood that attackers may intercept communications between them. This complexity presents significant challenges for maintaining security. For instance, inadequate encryption standards and weak device authentication methods can leave systems exposed. It's essential to implement robust firmware update protocols; without regular updates, vulnerabilities can persist over time.
Moreover, lightweight cryptographic algorithms are crucial for constrained devices where performance needs to be balanced with security measures. The integration of machine learning technologies plays a vital role in detecting anomalies and proactively identifying potential threats before they escalate.
Real-world examples illustrate how poor device configurations or a lack of consistent updates have led to severe vulnerabilities. These factors underscore the critical challenges facing IoT security today and highlight the need for comprehensive solutions to safeguard interconnected environments.
Effective Strategies to Protect IoT Systems
- **Remote exposure**: The internet connectivity of IoT devices creates a broader attack surface, making them more susceptible to remote hacking or phishing attempts.
- **Lack of industry foresight**: Sectors like healthcare and automotive increasingly depend on IoT technologies, yet they often fall short in terms of adequate security investments.
To address these vulnerabilities effectively, adopting strategies like defense-in-depth is crucial; this approach involves layering multiple security measures for enhanced protection. Utilizing hardware-based security features such as Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) or secure enclaves can significantly bolster device integrity. It's also important to prioritize regular firmware updates and manage patches diligently to fortify defenses against potential exploits. Moreover, implementing strong encryption protocols for both data transmission and storage will further strengthen overall security efforts. Lastly, fostering user awareness regarding potential threats is vital in cultivating a culture focused on cybersecurity vigilance among users.
Implementing Security by Design for Better Protection
Moreover, the interconnected nature of these devices can create significant risks. If one device is compromised, it may jeopardize the entire network since they often form a single point of failure. This situation underscores the importance of adopting comprehensive security measures from the outset—such as threat modeling and secure coding practices—as well as conducting regular security audits.
To enhance protection further, it's essential to consider using durable materials like tamper-resistant enclosures for physical safeguarding and customizable settings that allow for tailored encryption algorithms based on each device's capabilities and user privacy preferences. By integrating these elements into IoT designs, we can promote a more resilient approach to security in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Enhancing Network and API Security Measures
To effectively protect IoT systems and devices, cybersecurity professionals need to utilize a variety of tools and technologies. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. **Security by Design**: It's essential for companies to integrate security measures right from the initial design phase when developing IoT devices. This proactive approach can significantly reduce or even eliminate numerous vulnerabilities that could be exploited later on.
By adopting such measures, organizations can enhance their overall cybersecurity posture and better protect sensitive information transmitted by their IoT solutions.
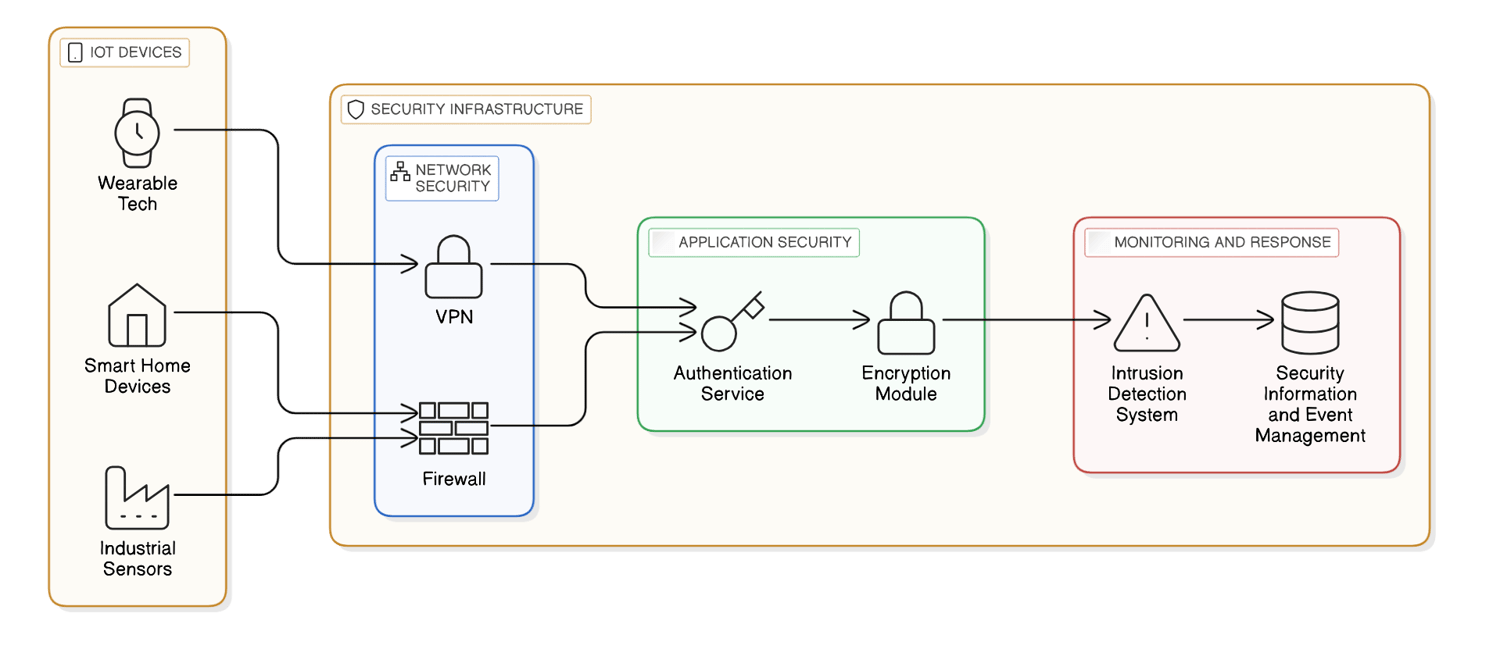
Additional Methods for Strengthening IoT Security
**2. PKI and Digital Certificates**: These refer to the methods used to secure connections between clients and servers by encrypting data, which is crucial for protecting transactions. This technology plays a vital role in areas such as e-commerce and communications within the Internet of Things (IoT).
**3. Network Security**: Safeguarding IoT networks involves a variety of strategies, including securing ports, utilizing firewalls, implementing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and blocking unauthorized IP addresses among other techniques.
**4. API Security**: It’s essential to ensure the security of data exchanged between IoT devices and back-end systems to prevent unauthorized access and breaches similar to those experienced by companies like T-Mobile. In addition to these measures, adopting practices like device hardening—minimizing unnecessary services and applying secure coding practices—can enhance protection. Strong encryption protocols should be utilized during data transmission to defend against potential eavesdropping threats. Regular firmware updates are crucial for addressing any vulnerabilities that may arise over time. Furthermore, segmenting the network can help isolate IoT devices from critical systems, thereby minimizing the risk of widespread attacks. Integrating anomaly detection systems can also assist in spotting unusual activities that might indicate a breach has occurred. Lastly, establishing strict access controls along with multi-factor authentication will provide an additional layer of security against unauthorized access.
The Growing Demand for Cybersecurity Professionals in IoT
Empowering users and employees through comprehensive cybersecurity training is essential in addressing IoT security challenges and understanding best practices. Adopting a zero-trust security model that enforces continuous verification and authorization can significantly bolster defenses.
Given that IoT devices have become integral to both our daily lives and business operations, they are increasingly targeted by cyber attackers due to their interconnected nature and the vast amounts of data they handle. By adhering to established cybersecurity best practices along with maintaining proper awareness through training, we can better protect our devices and sensitive information from threats.
As the significance of IoT cybersecurity continues to grow, there is an escalating demand for skilled professionals who specialize in this area. This underscores the importance of pursuing relevant certifications like Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or expertise in emerging technologies such as machine learning algorithms for threat detection or encryption protocols specifically designed for IoT environments. Additionally, familiarity with trends like edge computing is becoming vital as it reshapes security roles within organizations. Hence, acquiring skills that encompass both hardware vulnerabilities and software defenses will be key in advancing one’s career in this evolving field.
Reference Source
Top IoT Security Challenges and Best Practices
These measures include hardening devices, monitoring, updating firmware, managing access, responding to threats, and addressing vulnerabilities.
Source: BalbixIoT Security Best Practices? How To Protect IoT Devices
Protecting data storage includes effective, updated antivirus solutions and monitoring and scanning tools that cover the network against real-time IoT threats.
Source: FortinetIoT Cybersecurity: Strengthening Defenses against Threats
To protect IoT systems, both devices and infrastructure should be properly secured. Often, it is necessary to update passwords, encrypt data, and implement ...
Source: American Public University10 Tips to Secure Your IoT Devices from Hackers
Protecting your IoT device starts with establishing password security measures as the cornerstone of defense against potential breaches by cyber attackers who ...
Source: IoT For AllIoT Device Security: Enhance Protection Against Cyber Threats
To counter these threats, using strict access control for IoT network security is crucial. By enforcing role-based access control, firewall protections, and ...
Source: sepiocyber.comTop 10 Strategies for Ensuring IoT Security
Using tamper-resistant hardware and secure enclosures can prevent unauthorized physical access to devices.
Source: AerisHow to Secure IoT Devices in the Enterprise
Protect IoT devices in your enterprise. Learn best practices for securing connected devices, preventing cyber threats, and ensuring data privacy.
Source: Palo Alto NetworksTop 10 IoT Security Risks and How to Mitigate Them
Explore the top 10 IoT security risks, effective mitigation strategies, and best practices to secure IoT devices against cyber threats.
Source: SentinelOne


 ALL
ALL Smart Ecosystem
Smart Ecosystem
Related Discussions